- Home /
- Resources /
- Learning center /
- Devices on Multipl...
Devices on Multiple VLANs with Full IP Control and Connected to multiple Cloud Providers' VPC Subnets
Networking Architecture - Creating a network where devices are linked on a shared layer 2 VLAN with full IP control, directly connected to subnet in multiple VPCs on multiple cloud provider.
On this page
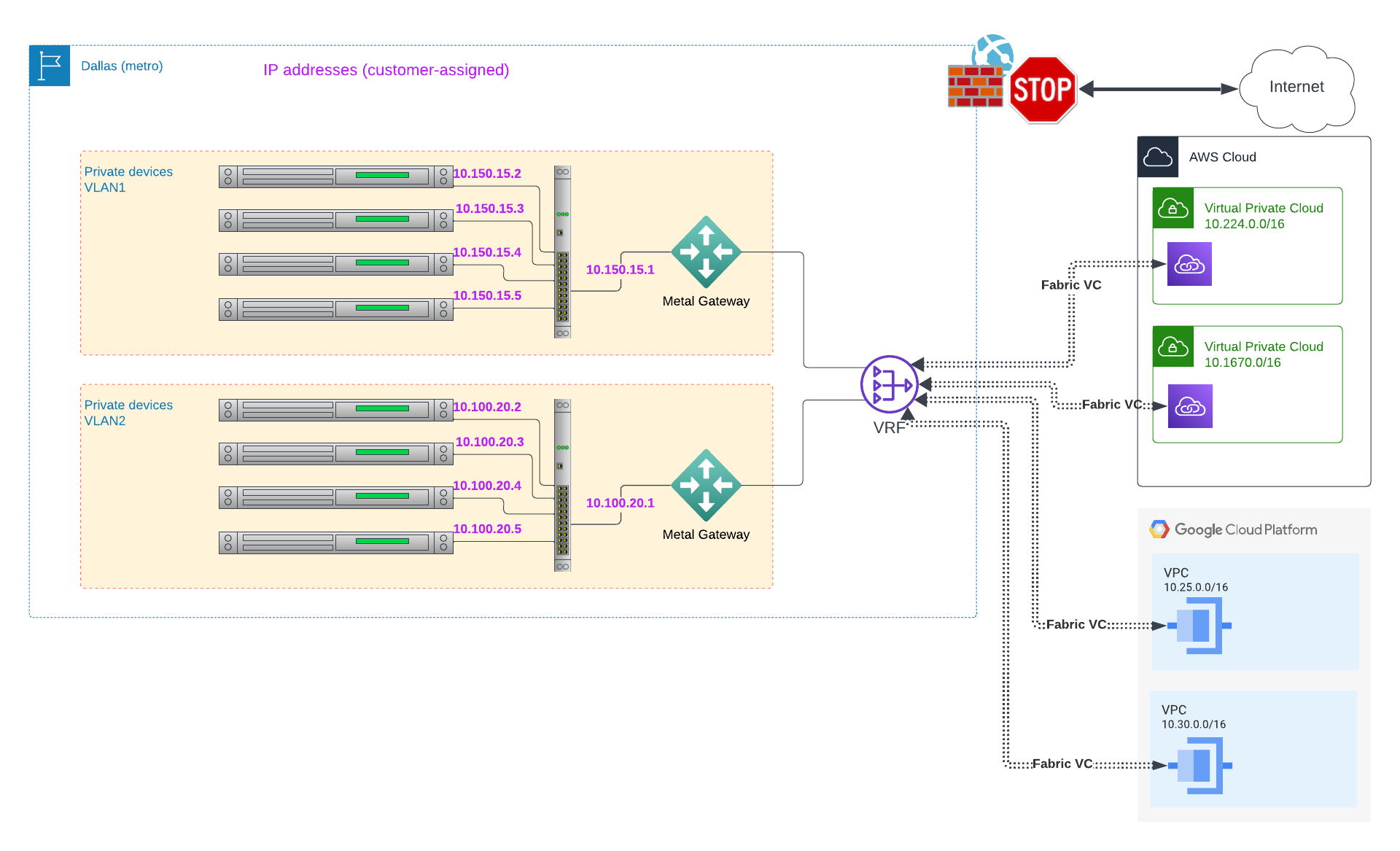
Imagine this situation: You have one or more isolated VLANs. All of your devices are on those VLANs, and can communicate at Layer 2 with other devices on the same VLAN. Those devices can communicate privately with servers and services in subnets in multiple VPCs on your cloud providers, and on the other VLAN. The VPCs and subnets have address ranges distinct from each other, as well as from the VLANs, and therefore communication happens over layer 3, that is, routing.
In this scenario:
- No devices are connected directly to the internet; there are no internet connections at all
- No devices are connected directly to Equinix Metal's private network
- Devices communicate with each other using shared Layer 2 VLANs
- Devices use private IPs allocated by you and not by Equinix Metal
- Devices connect to subnets in multiple VPCs on your cloud providers
- Each subnet, whether in cloud provider VPCs or in Metal VLANs, is in unique IP range
The devices receive no private or public IP addresses from Equinix Metal. Your network setup looks like this:
Equinix Fabric and Equinix Virtual Routing and Forwarding for Security
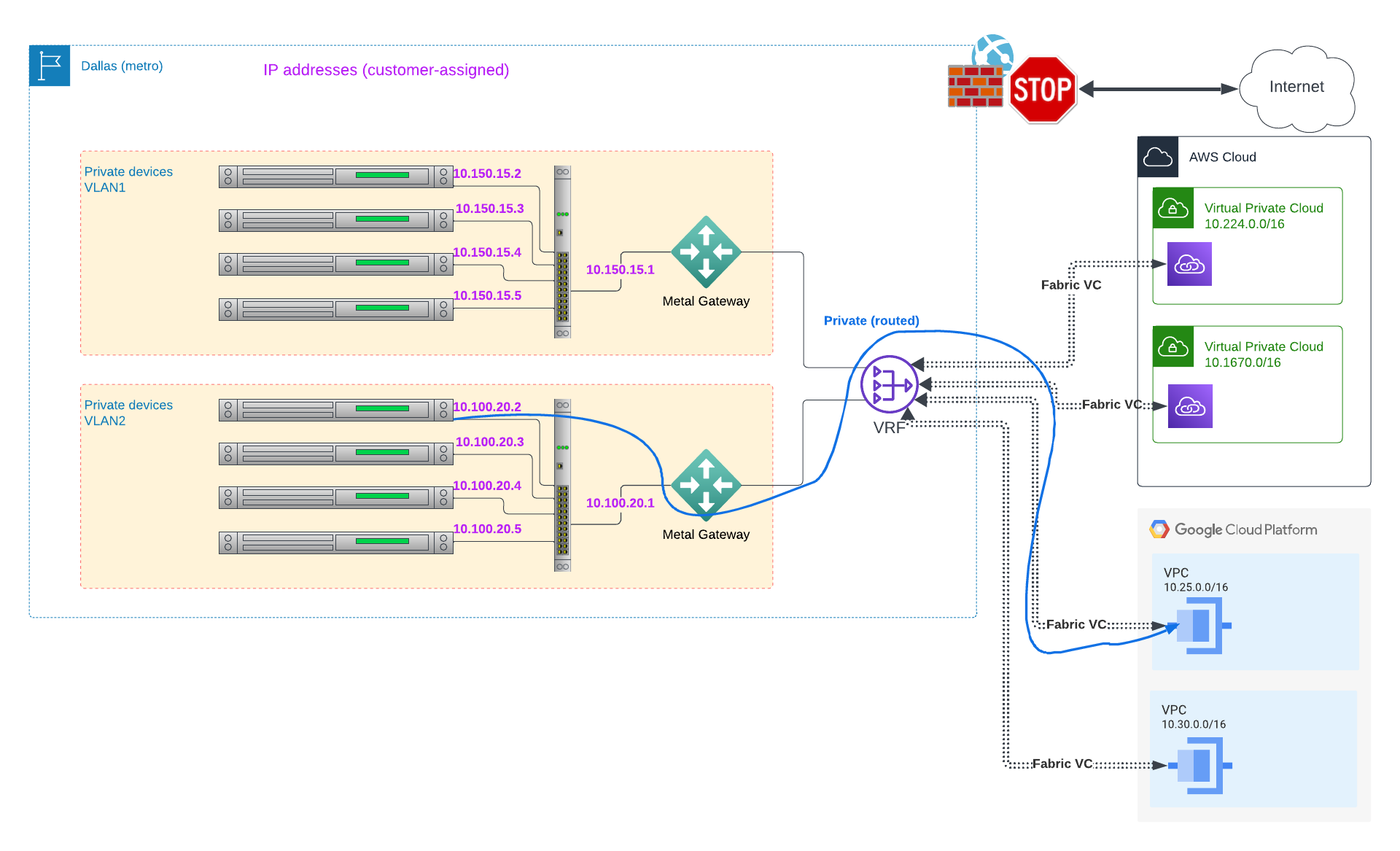
As you have multiple networks - VPCs in cloud providers, VLANs in Equinix Metal - you need two things to be able to send traffic between them:
- Connectivity: actual networking connectivity between the networks: You need Equinix Fabric
- Routing: knowledge of how to route traffic between the networks: You need Virtual Routing and Forwarding
Equinix Fabric is the connectivity between the cloud providers and Metal VLANs. You deploy a Virtual Connection (VC) to link each pair of one of the VLANs, via a Metal Gateway, with each cloud provider. Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) provides the routing functionality between the pairs of networks over the Fabric VC. You deploy a single VRF that handles all of the connections.
Setting up Equinix Metal Virtual Routing and Forwarding
First, you'll need to configure Equinix Metal Virtual Routing and Forwarding. Follow these steps:
- Select a unique IP range for each VLAN, distinct from the IP ranges in use in your VPCs or other VLANs.
- Deploy Equinix Metal VRF. Ensure that your
allowed_ipsranges cover the IP ranges that you will use on all of your VLANs. - Reserve the IP ranges for each of your VLANs from inside the VRF configuration, using
ip_reservations.
Connecting the VLANs to Equinix Fabric
With the VRF created, follow theses steps for each VLAN:
- Create the VLANs.
- Create a Metal Gateway, attached to the VLAN and the single VRF.
- Create as many devices as you desire, without a public or private IP address but connected to the VLAN. For each device:
- Retrieve the port ID for the network port, using the Equinix Metal console or API.
- Assign that network port to the VLAN, using the Equinix Metal console or API.
- SSH into the device, assign an IP address of your choosing, and set the default route of the device to the previously retrieved
"gateway"address for the IP reservation.
Then, for each for each cloud provider VPC, deploy an Equinix Fabric Virtual Connection (VC) between the VRF and the VPC subnet.
Conclusion
When you need a really secure network, but your devices still need to communicate, your options are limited. Equinix Fabric combined with Equinix Metal Virtual Routing and Forwarding provide the solution you need to be certain that your devices are only communicating with the devices that you want them to.
You may also like
Dig deeper into similar topics in our archives
Configuring BGP with BIRD 2 on Equinix Metal
Set up BGP on your Equinix Metal server using BIRD 2, including IP configuration, installation, and neighbor setup to ensure robust routing capabilities between your server and the Equinix M...
Configuring BGP with FRR on an Equinix Metal Server
Establish a robust BGP configuration on your Equinix Metal server using FRR, including setting up network interfaces, installing and configuring FRR software, and ensuring secure and efficie...
Crosscloud VPN with WireGuard
Learn to establish secure VPN connections across cloud environments using WireGuard, including detailed setups for site-to-site tunnels and VPN gateways with NAT on Equinix Metal, enhancing...

Deploy Your First Server
Learn the essentials of deploying your first server with Equinix Metal. Set up your project & SSH keys, provision a server and connect it to the internet.