- Home /
- Resources /
- Learning center /
- Intro to Virtual R...
Intro to Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
Introduction to Equinix Metal Virtual Routing and Forwarding

On this page
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) helps you connect your Layer 2 VLANs to other networks: Equinix colocation ports, cloud provider VPCs, or SaaS providers.
Part 1 of this series, Intro to Metal Gateway, explained how servers in Equinix Metal can be networked in one of two modes: the default Layer 3 mode, or on your own private Layer 2 VLAN.
With a VLAN, your network is fully isolated from any external connections, unless you create dedicated servers, configured in hybrid networking mode, to route between the Equinix Metal Layer 3 network and your private VLAN.
Metal Gateway is Equinix's managed virtual router to connect your VLAN to other networks.
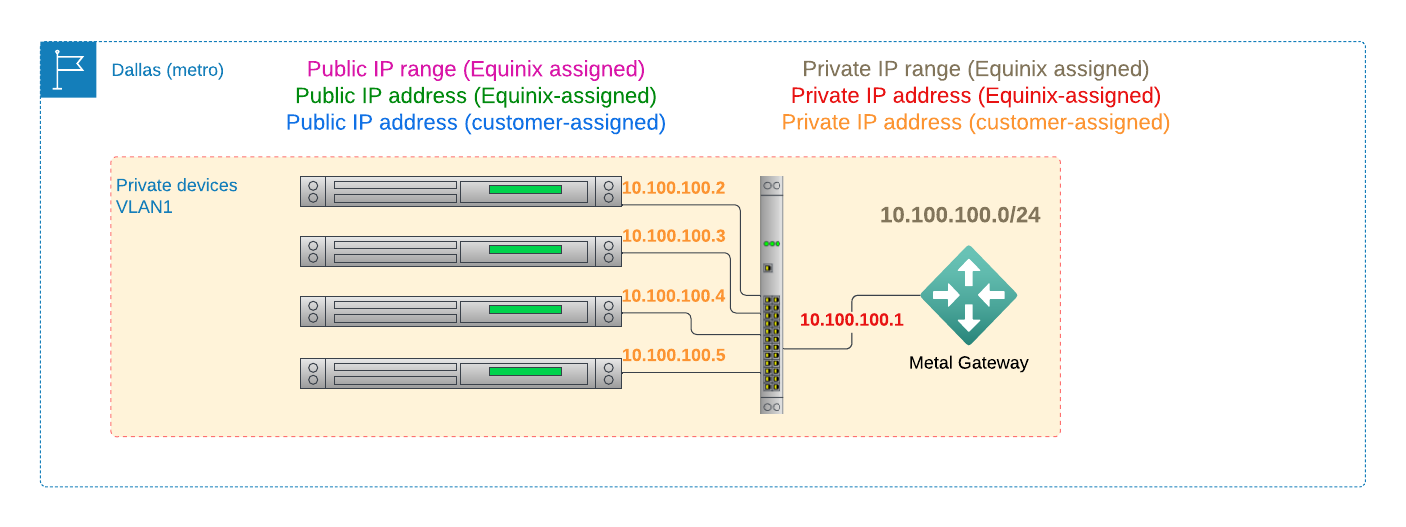
In this guide, you will learn about VRF, which completes the capabilities of Metal Gateway, enabling a fully interconnected network between your VLANs and other networks.
Interconnection basics
When you want to interconnect two networks, you need two things between them:
- A connection
- Traffic routing information
Connection
A connection is composed both of the physical wires that connect your networks, as well as the configuration that enables traffic to flow between them.
All servers in Equinix Metal are connected to their upstream routers, and from there to the global Equinix Metal network. When you deploy servers in the same metro and project, Equinix Metal configures the network so that they can send traffic to each other.
If you want to connect your VLAN at Equinix Metal to a VPC at a cloud provider or a port at an Equinix colocation facility, you use Equinix Fabric. Fabric already has the physical wires connecting between the Equinix Metal metro and the remote locations. Creating a Virtual Connection configures Fabric to allow network traffic to flow between the two sides of the VC.
Traffic routing information
A connection is necessary, but it is not sufficient. Even after you connect two or more routers, each router needs to be informed where to send traffic.
For example, if you create a connection between a VLAN's Metal Gateway and an AWS Transit Gateway in a VPC via a Fabric VC, the Transit Gateway needs to know which IP ranges the Metal Gateway can handle, and the Metal Gateway needs to know which IP ranges the Transit Gateway can handle. This becomes even more important when you have not two sides to the connection, but multiple VPCs, multiple colocation ports, and multiple Metal Gateways.
Virtual Routing and Forwarding
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) provides the traffic routing information between Metal Gateway and the router on the remote end. You can think of Gateway and VRF as partners.
- Gateway provides the router connection between your Layer 2 VLAN and the Layer 3 routing world
- VRF provides the Layer 3 configuration, announcing routes and receiving route announcements
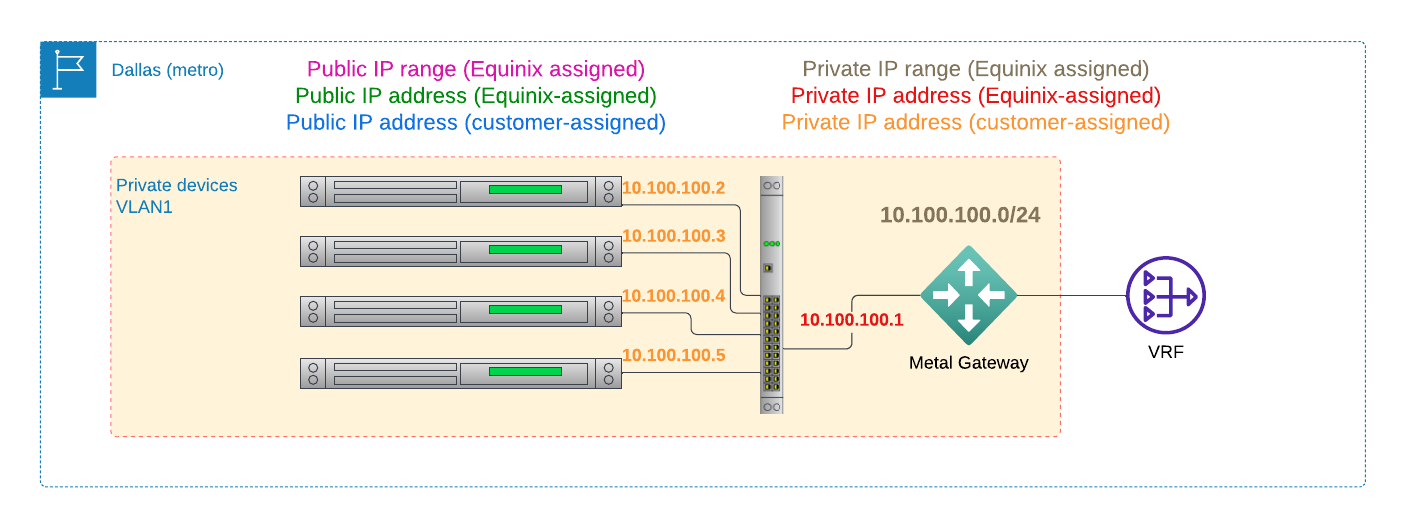
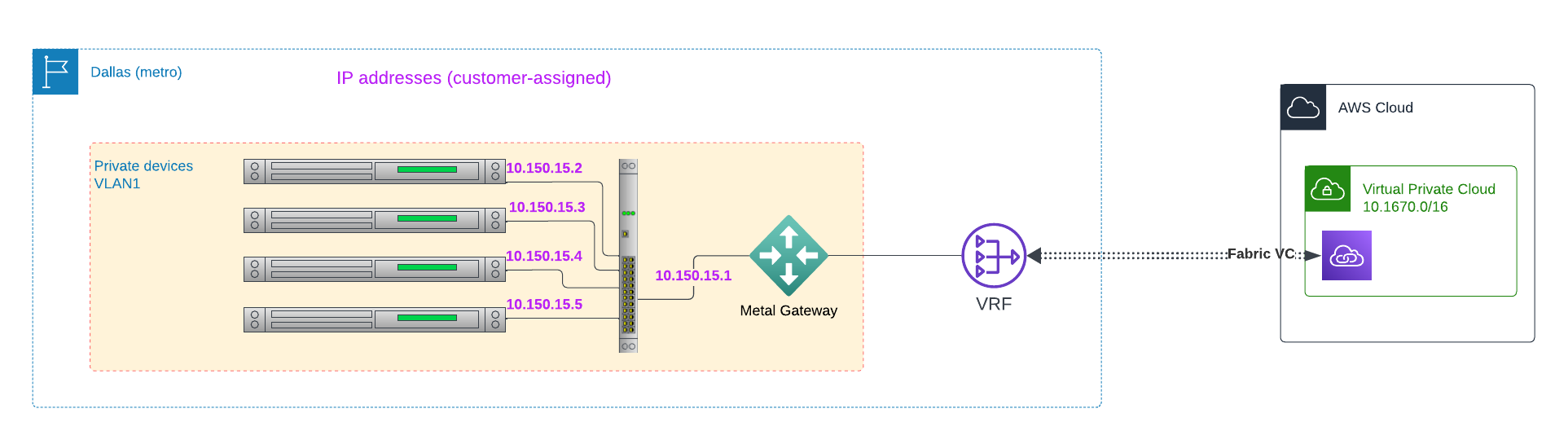
VRF can connect your VLAN, via your Gateway, over Fabric, to a cloud provider such as AWS:
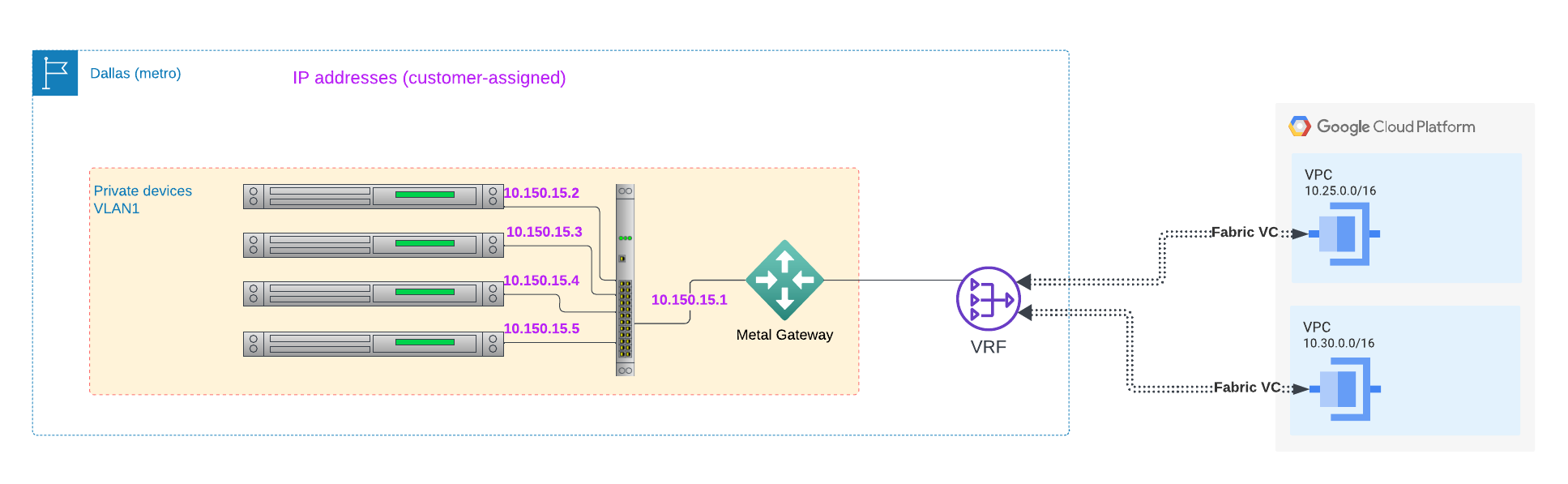
or Google Cloud:
It can connect your Gateway to an Equinix colocation port:
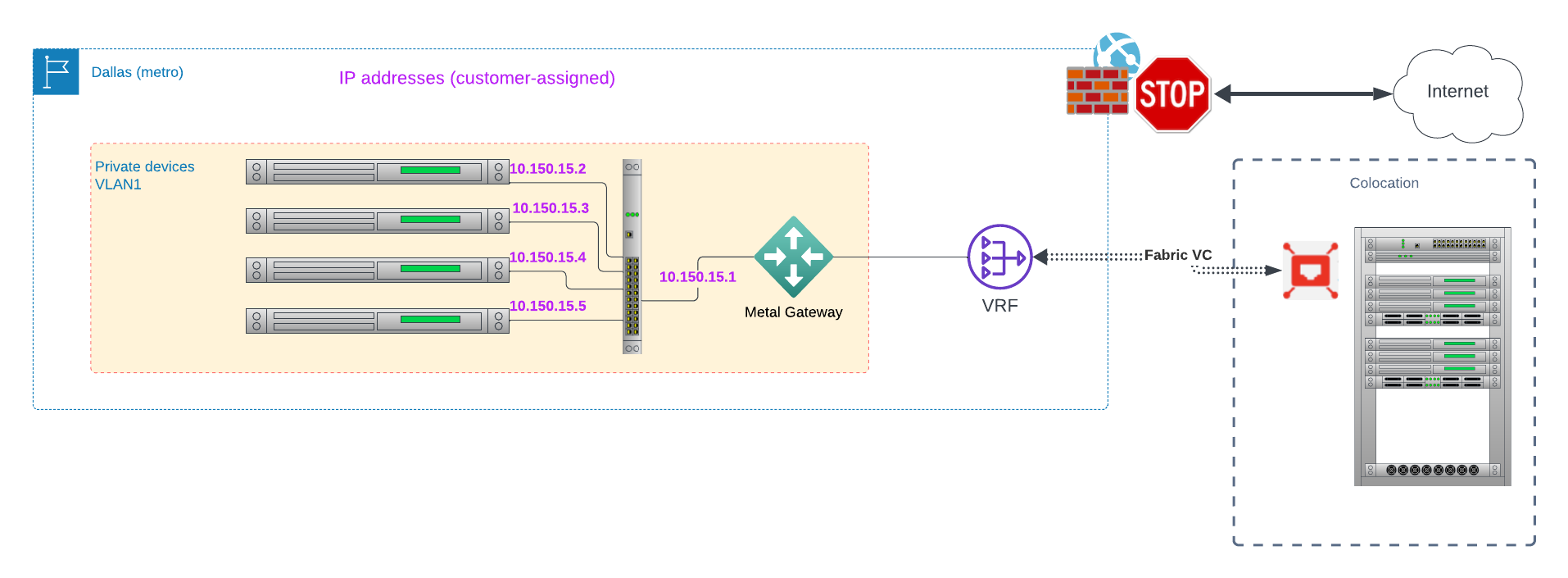
or to a SaaS provider:
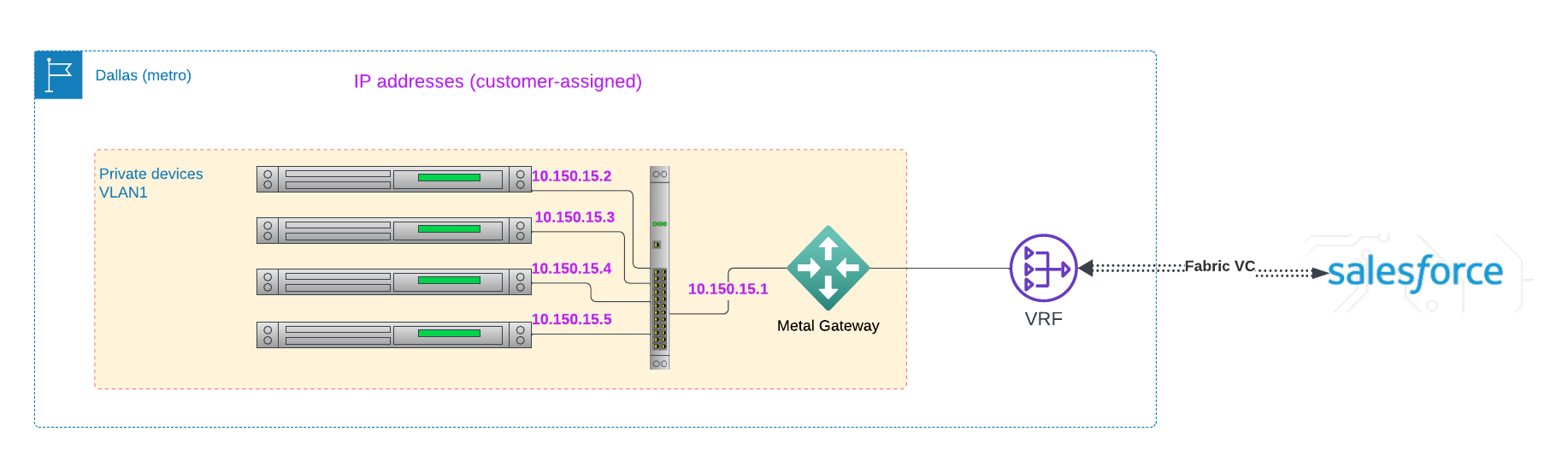
Multiple Gateways, Single VRF
A VLAN does not require a Metal Gateway to operate. Without a Gateway, all traffic simply flows along Layer 2 between the servers connected to the VLAN.
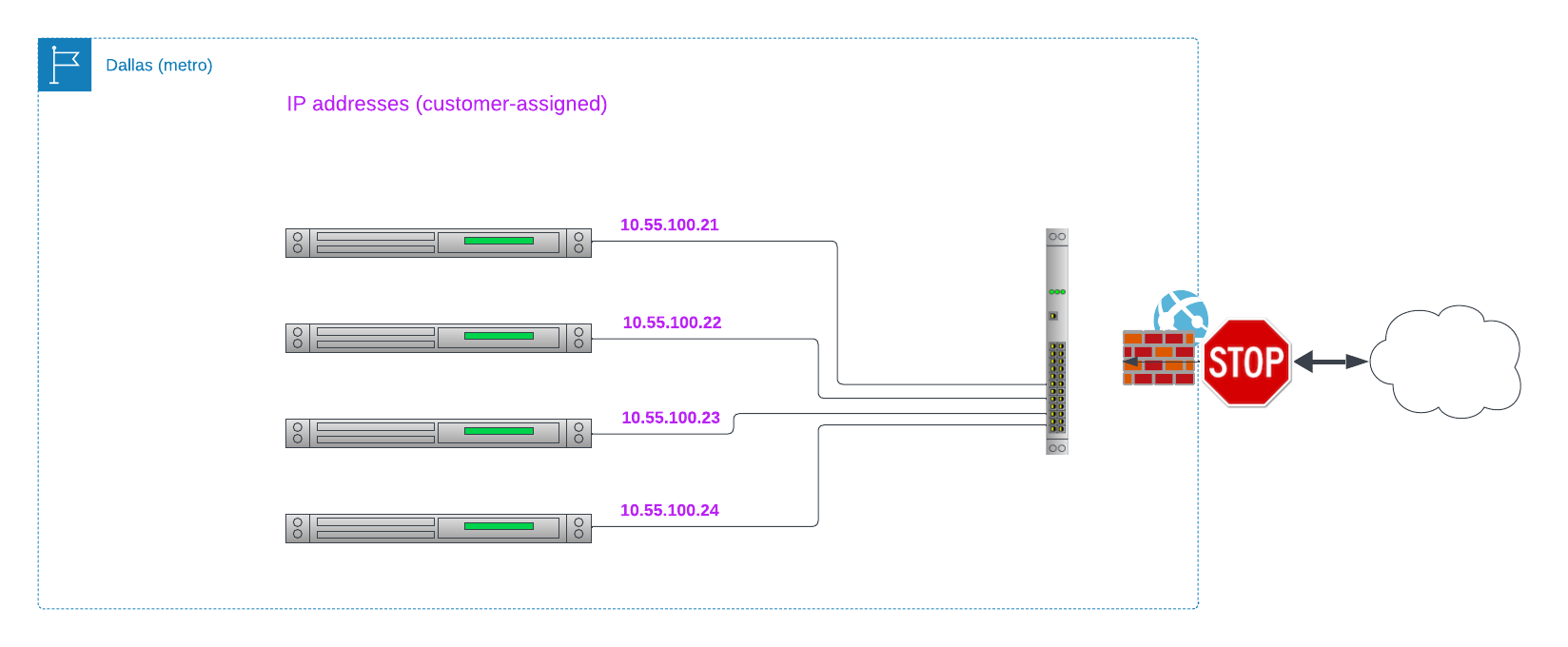
You can add one or more Gateways to a VLAN, each with its own purpose and IP range:
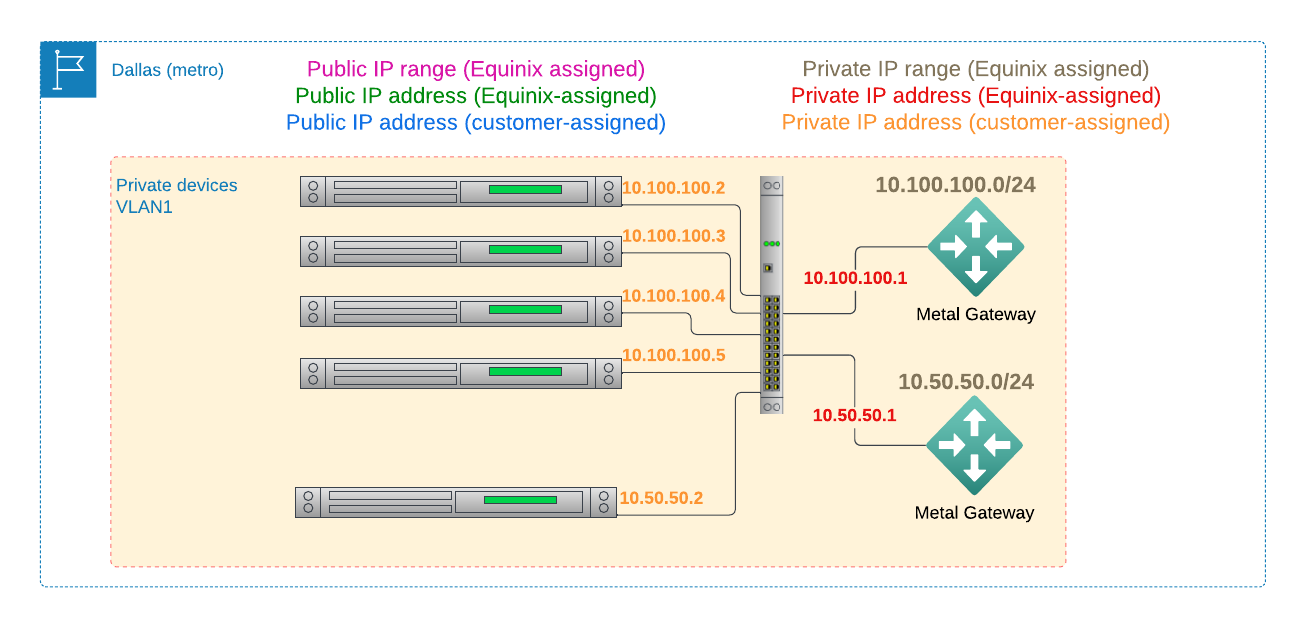
From within the console, two Metal Gateways on a single VLAN look like this:
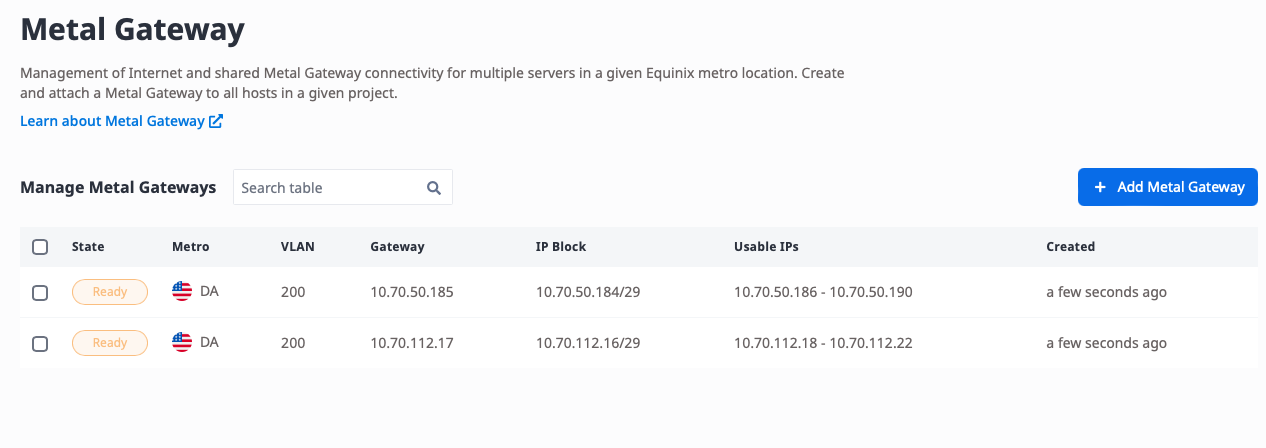
However, unless each serves an entirely different purpose, multiple Gateways often aren't necessary. When you connect a Gateway and a VRF, the VRF can connect to multiple remote locations:
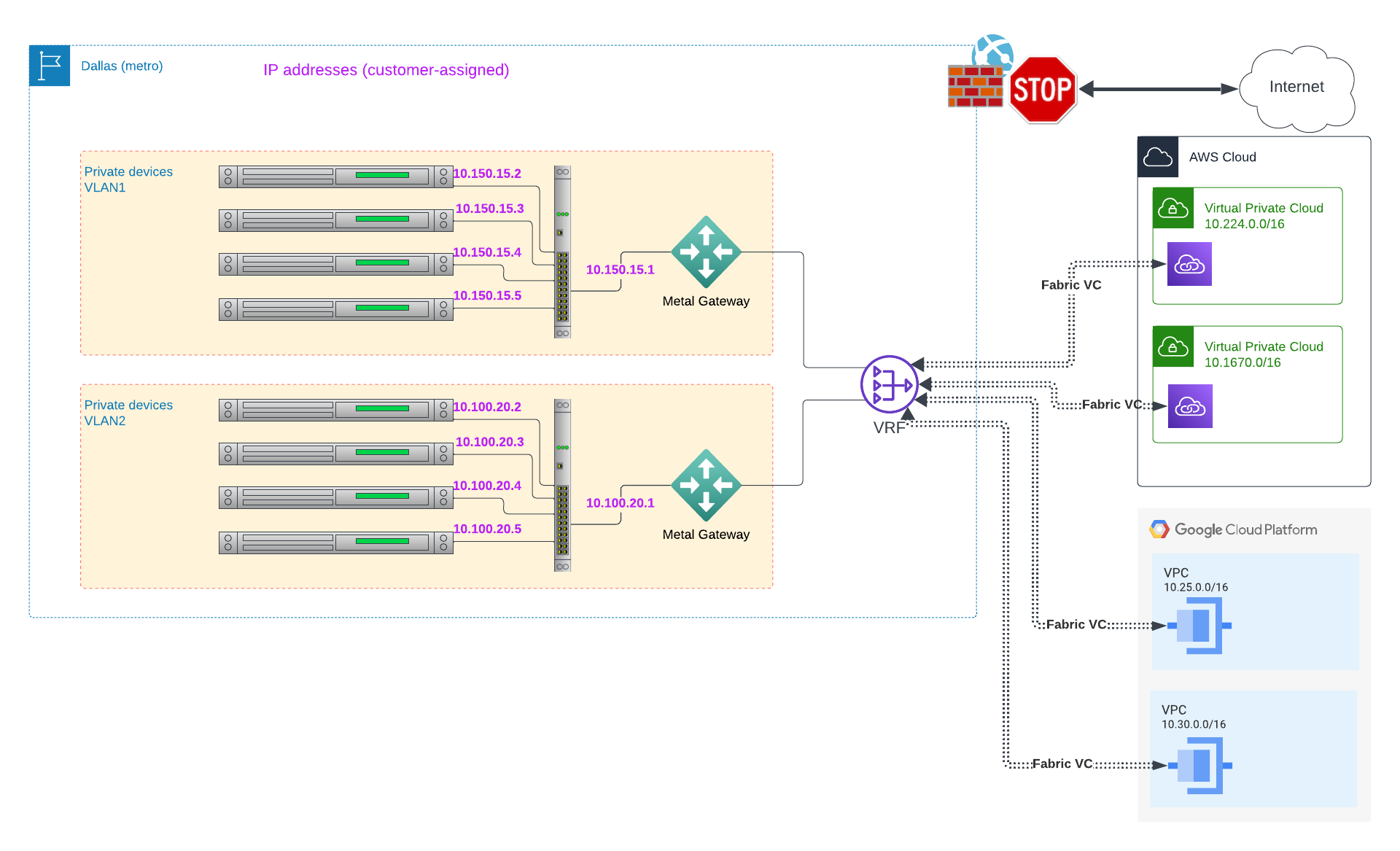
Each Gateway can connect to exactly one VLAN, and either an Equinix Metal-provided IP range, public or private, on the Equinix Metal network, or to a single VRF. That VRF, in turn, can connect to multiple Fabric VC, providing a simple way to connect your VLAN to multiple cloud provider VPCs, SaaS providers, and Equinix colocation ports.
Summary
Virtual Routing and Forwarding is the "router configuration" component that lets you connect and configure your Layer 3 Gateway to one or more remote locations.
You can connect a single Gateway to just a single VRF, but each VRF can connect to one or multiple remote connections.
You may also like
Dig deeper into similar topics in our archives
Crosscloud VPN with WireGuard
Learn to establish secure VPN connections across cloud environments using WireGuard, including detailed setups for site-to-site tunnels and VPN gateways with NAT on Equinix Metal, enhancing...
Kubernetes Cluster API
Learn how to provision a Kubernetes cluster with Cluster API
Kubernetes with kubeadm
Learn how to deploy Kubernetes with kubeadm using userdata

OpenStack DevStack
Use DevStack to install and test OpenStack on an Equinix Metal server.