- Home /
- Resources /
- Learning center /
- Amazon EKS-Anywher...
Amazon EKS-Anywhere on Equinix Metal
Tested in Equinix Metal, providing the extension of the environments in hybrid mode between AWS and our BMaaS.
On this page
EKS Anywhere allows you to create your own EKS clusters outside of AWS.
You can run EKS Anywhere directly on bare metal, without needing to run it in a virtualized environment. To test out our EKS-A deployments, check out our EKS-A Terraform repository in GitHub. It contains both manual setup instructions and automation for running EKS Anywhere on bare metal.
In this guide, you'll deploy EKS Anywhere on a virtualized environment layer on top of Equinix Metal, providing an extended environment in hybrid mode between AWS and your platform.
Additionally, you'll learn how to keep the communication private and secure between both sides using Network Edge, skipping the connection through the internet.
You will need
- An AWS account
- An Equinix Fabric account, with Network Edge services enabled
- An Equinix Metal account
- A Billing Account in Equinix
Managing the environment
There are three different parts to this deployment. The first is to set up connectivity between the Equinix Metal service and AWS using a Network Edge appliance. If you're looking for an ECS connection, see the tutorial AWS ECS Anywhere on Equinix Metal.
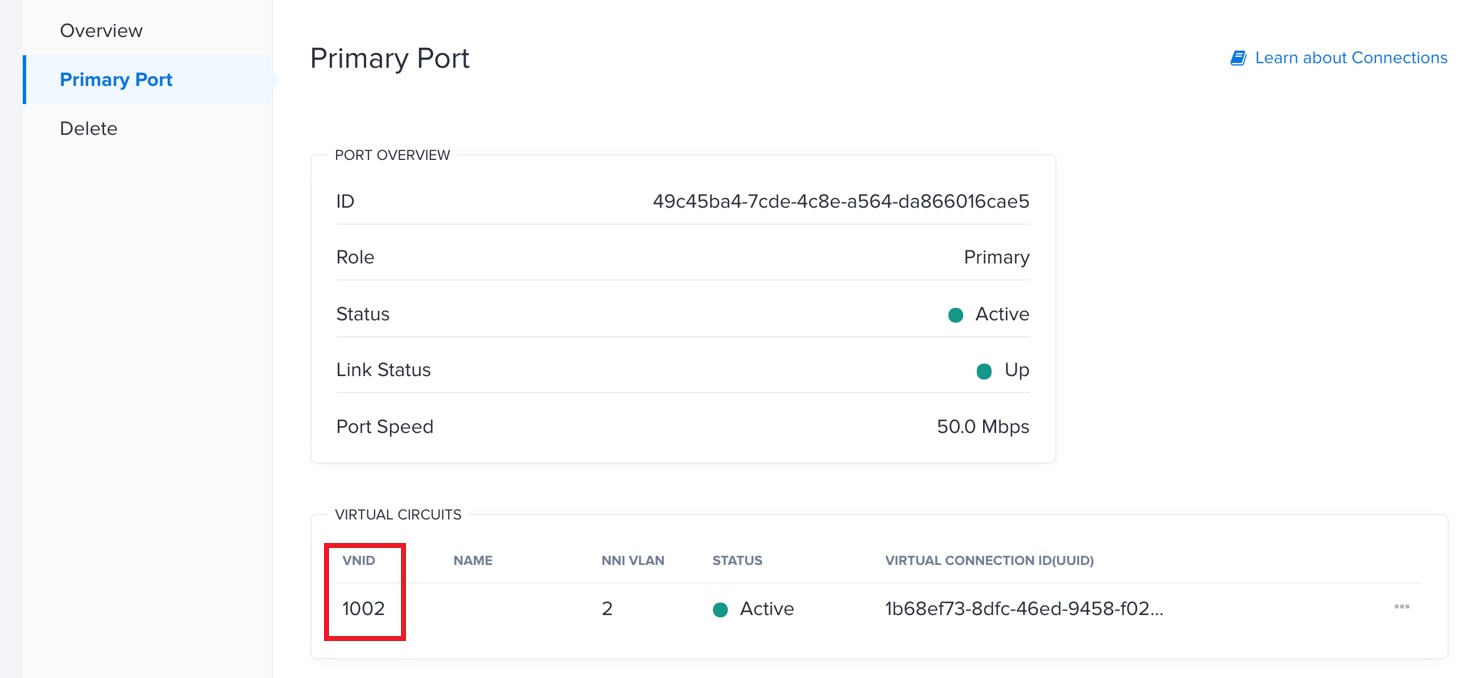
As the ECS guide explains, you need to verify that the VLAN that you are linking to the primary port is attached to the ESXi host as well, in order to achieve private connectivity between ESXi hosts and AWS, as shown here:
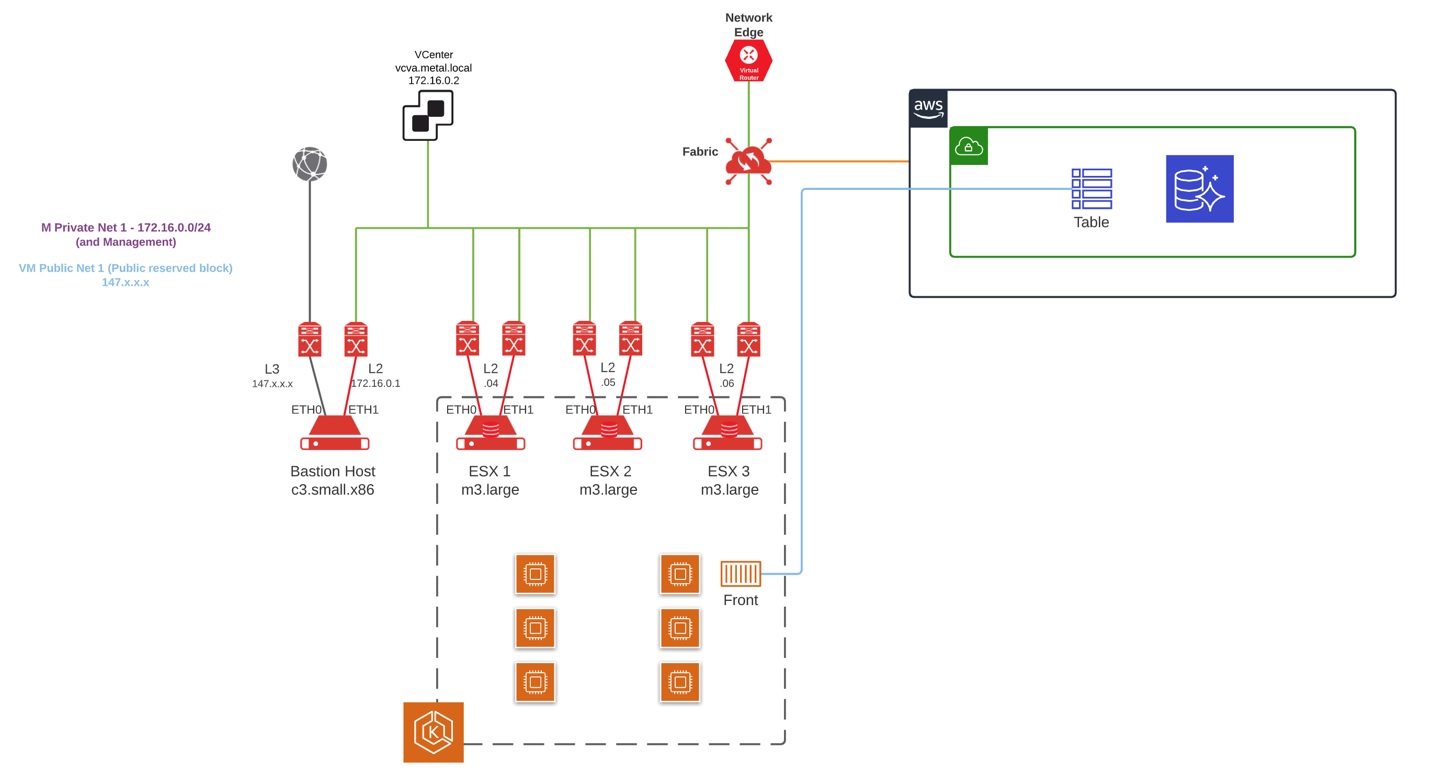
The second part is to configure the servers to create a private cluster but with a bastion host that allows you to interact during the EKS-A cluster installation. For this specific purpose the network model used for bastion host is Hybrid mode, and for the ESXi hosts is Layer2. See the Equinix Layer 2 Networking Index for more details. The network architecture will look like this:
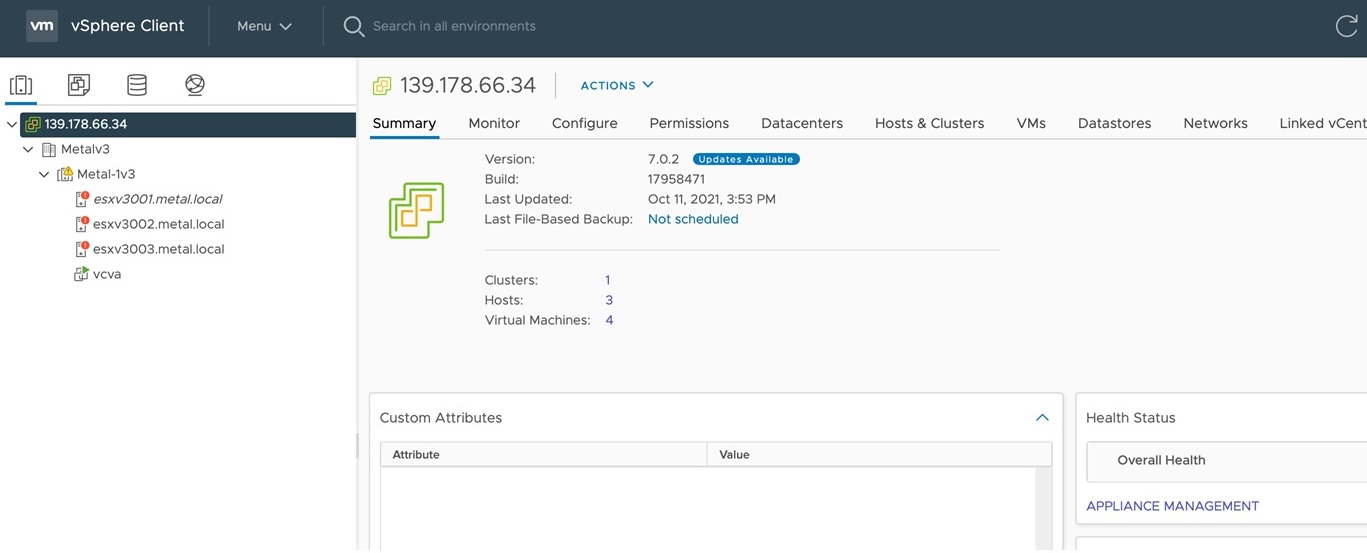
The third part is the deployment of the virtualization solution at the top of Equinix Metal. Equinix offers VMware VCF for Metal servers. After both deployments are in place your vSphere console will look like this:
Now that the virtual environment is set up, you can install the EKS-Anywhere deployment from the bastion host server.
EKS-A deployment
You can use your bastion host as administrative machine to run the EKS Anywhere installation. Follow this AWS EKS-A binary guide installation to set up the environment before the cluster creation.
After the environment is set up, follow the AWS guide for EKS-A cluster creation.
Once that's done, access the vSphere console, which will look something like this:
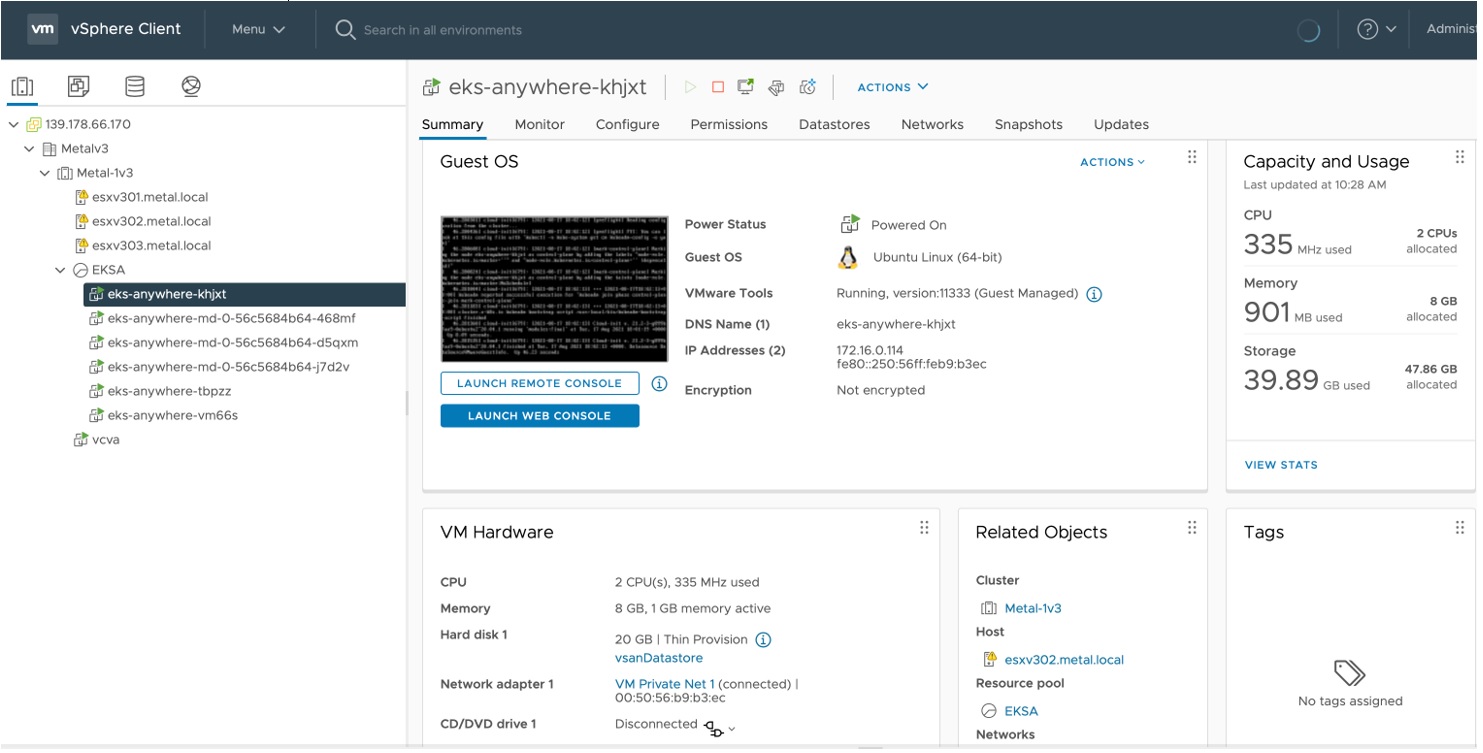
You can see the EKS Anywhere cluster components in the list on the left.
Make sure you have kubeconfig set up on the bastion host. Once that's done, you can use kubectl to get information about the cluster nodes:
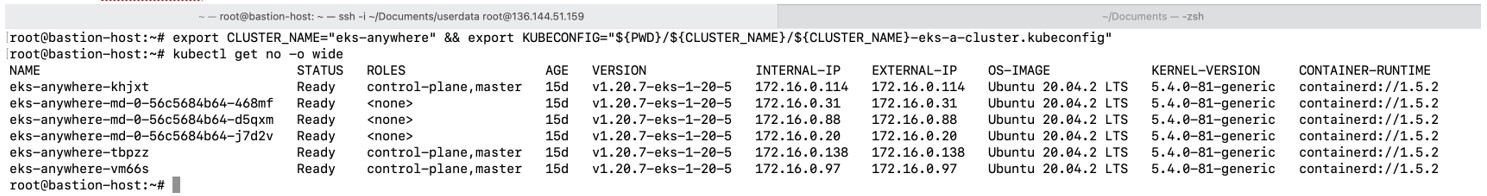
If kubectl show that the cluster nodes are ready, the cluster is fully operational. AWS also provides a deployment workload test to ensure the cluster is working properly.
If you run into any problems, you can check out the troubleshooting section from the EKS Anywhere home page.
Private connection and routing
You deployed the Network Edge appliance and the connections to Metal and AWS in the "Managing the environment" section at the beginning of this tutorial. Now you'll add the static route to the ESXi hosts to be able to route the traffic from the workloads on Metal to AWS. Use this command to do so:
route add -net [aws_private_network_cidr] netmask [aws_private_network_mask] gw [vmware_private_network_gateway]
Where:
-
aws_private_network_cidris the IP range for your subnet in AWS -
aws_private_network_maskis the netmask for your subnet in AWS -
vmware_private_network_gatewayis the gateway defined for the private network in the VMWARE environment. This network is defined with the same VLAN connected to the Network Edge device in the Metal connection.
Now you can use private routing for the resources you want to consume on AWS and the traffic will be routed over the direct and secure Equinix connection.
Testing the private connectivity
You now have a container-based application that displays a page with the result of a database query and you've directly configured private access to the resource.
The database is MYSQL from the AWS RDS service, to which only private access is allowed. You'll run the application from the EKS cluster on Equinix Metal and without querying the AWS service:
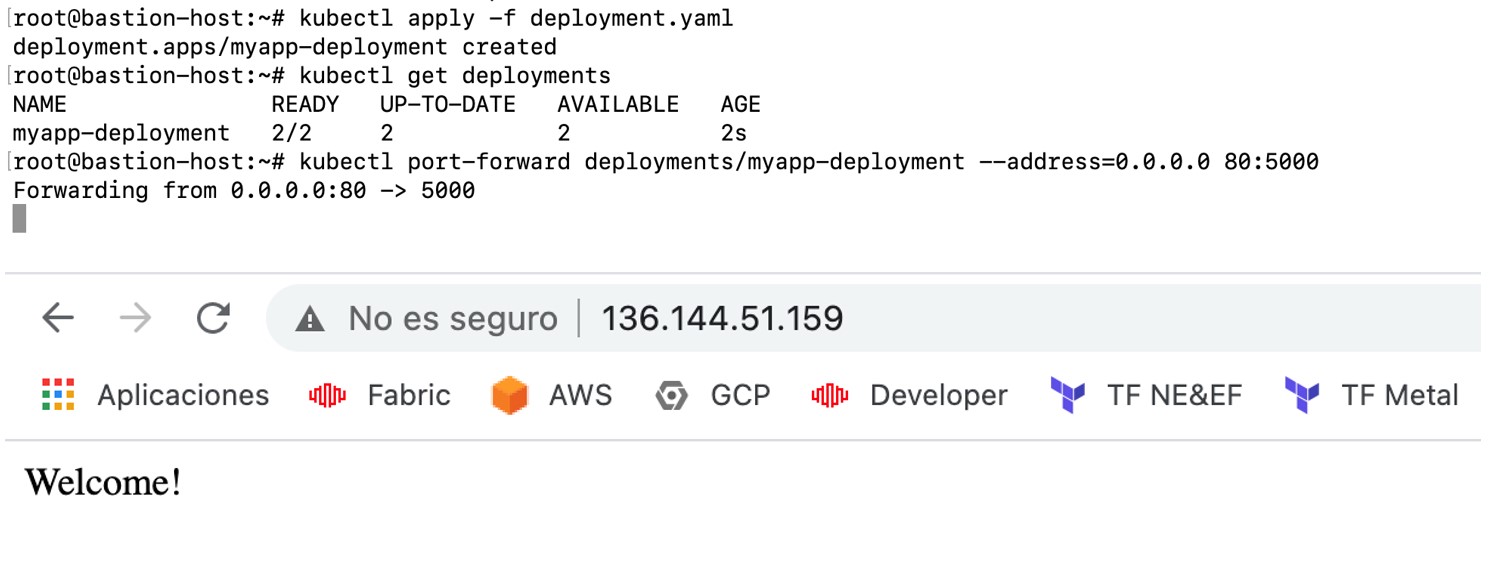
Now you can query the RDS table using the private connection previously created: 
Conclusion
EKS Anywhere allows you to migrate your EKS workloads to Equinix Metal. You need to define the private connection from Metal to your virtual network device (as in this example) or your Equinix Fabric port and connect directly to AWS services.
After installing the cluster on the virtual environment, you add the routes to the Amazon private space. Then you communicate with the resources in AWS in the same way you were doing it working directly on a cluster in the cloud.
You may also like
Dig deeper into similar topics in our archives
Crosscloud VPN with WireGuard
Learn to establish secure VPN connections across cloud environments using WireGuard, including detailed setups for site-to-site tunnels and VPN gateways with NAT on Equinix Metal, enhancing...
Kubernetes Cluster API
Learn how to provision a Kubernetes cluster with Cluster API
Kubernetes with kubeadm
Learn how to deploy Kubernetes with kubeadm using userdata

OpenStack DevStack
Use DevStack to install and test OpenStack on an Equinix Metal server.